robot ballboy

Welcome back my nerdy friends!
Today’s edition is buzzing with so many new readers and winners.
And the mystery gift this time around will be delivered to the first 20 people only
(if you haven’t got your mystery gift yet, pls reply (im sorry if i missed it 😢))
Many replied but none got all three correct, 2 out of 3 is good enough for me!
(Oh btw the answers were: True<False<True)
Want to be featured in the next edition? And win your mystery gift?
Reply with the answer to this: Let’s get into this week’s game!
Engineering "This or That":
Pick the RIGHT answer for each scenario:
Question 1: To increase the strength-to-weight ratio of a steel beam, engineers:
Make it hollow (I-beam shape) OR Make it solid and rectangular?
Question 2: In a transformer, to step UP voltage from 120V to 240V, the secondary coil has:
More wire turns than primary OR Fewer wire turns than primary?
Question 3: When engineers design gear systems for high torque applications, they use:
Larger gear teeth OR Smaller gear teeth?
Know the answers?
Want to reach an audience of over 80k engineers? Click here to book a call with me to see how we can partner to help!
What Happened This Week?
1. Gold Nanoparticles Deliver Lithium to Your Brain Through Your Nose (I'm Not Making This Up)
Okay so lithium is literally one of the best known treatments for bipolar disorder and Alzheimer's, but here's the catch: it slowly destroys your kidneys and thyroid. You're basically choosing between a functional brain and functional organs. Great options, right?
Italian researchers chose to bypass the whole digestive system entirely by creating a nasal spray with gold nanoparticles. Yes, GOLD. In your NOSE.
The setup is weirdly cool?
They coat microscopic gold particles with lithium and this helper molecule called glutathione. You spray it up your nose, and boom: the particles travel straight through your nasal passages into your brain. The glutathione acts like a backstage pass getting them into cells, then the gold breaks down and releases lithium exactly where you need it.
Compare that to swallowing pills where the lithium goes through your entire bloodstream hitting every single organ like "hello kidneys, hello thyroid, hey liver what's up" before finally reaching your brain. Not what you’d want lol.
They tested it on mice with Alzheimer's and their memory came back with ZERO side effects. Manufacturing is cheap, it's already patented, and honestly I can't believe the solution was just "use your nose" this whole time..
2. Batteries That Heal Themselves? China Just Made It Happen
Remember the idea of ejectable batteries a few editions ago?
China already found a fix that doesn’t involve hurting others.
Solid-state batteries have been "5 years away" for like 40 years now.
They promise phones lasting days and EVs going 3x farther, but they keep failing because the layers inside literally fall apart over time like a sad sandwich.
Chinese scientists just cracked it with iodine ions that automatically fix cracks as they form. I'm still processing how clever this is.

Solid-state batteries use solid stuff instead of flammable liquid (already better), which lets them pack 2-3x more energy. The problem is when you charge them, materials expand and contract creating microscopic gaps. These gaps are battery killers.
The solution? Add iodine ions to the mix. During operation, these ions are like "oh there's a crack forming" and migrate over to fill it automatically. They form this thin healing layer that attracts lithium ions and seals everything up in real-time. Current solid-state batteries need FIFTY ATMOSPHERES of pressure crushing them just to stay functional. This design needs... zero. Nothing. It just works.
If this scales up, we're talking phones that last for days and EVs that finally make gas cars look stupid. Batteries that fix themselves while you sleep? Yeah, I'll take that. What about you?
3. This Robot Picks Up Tennis Balls Better Than I Ever Could
LimX Dynamics posted a video of their humanoid robot Oli picking up tennis balls, and I'm lowkey jealous of how smooth it moves. BECAUSE it’s not controlled by a joystick or a programmer typing commands. Instead, it’s got its own brain.
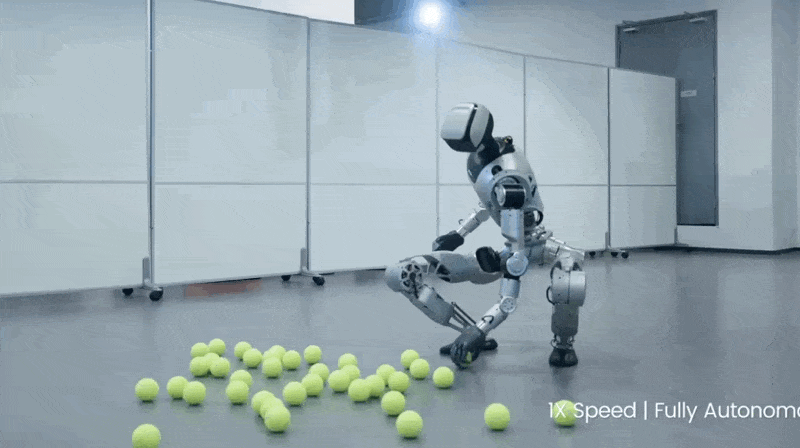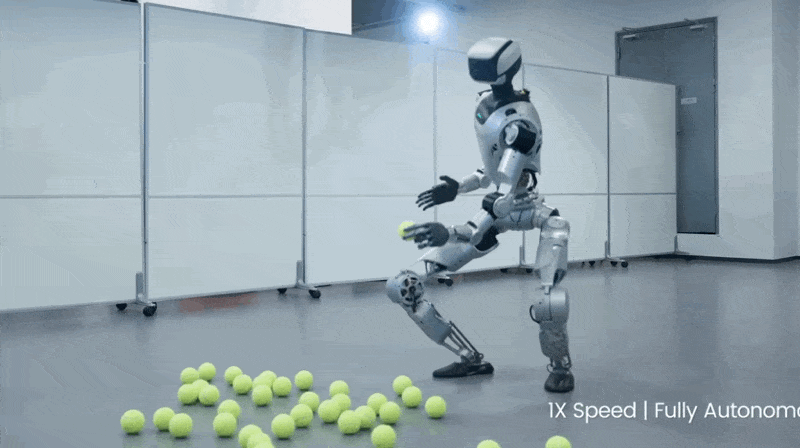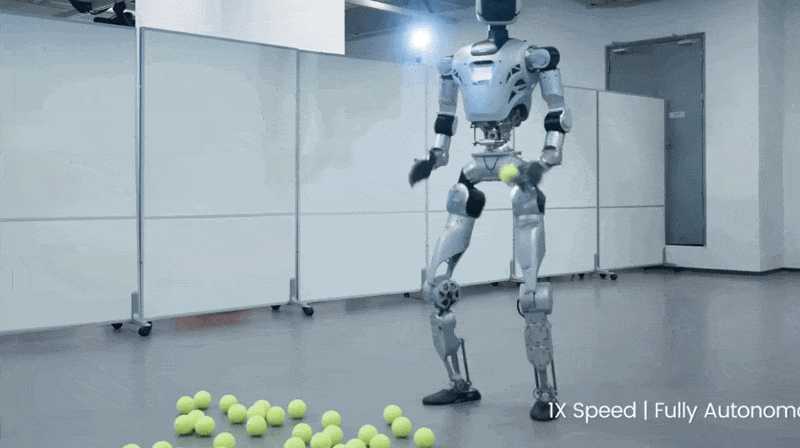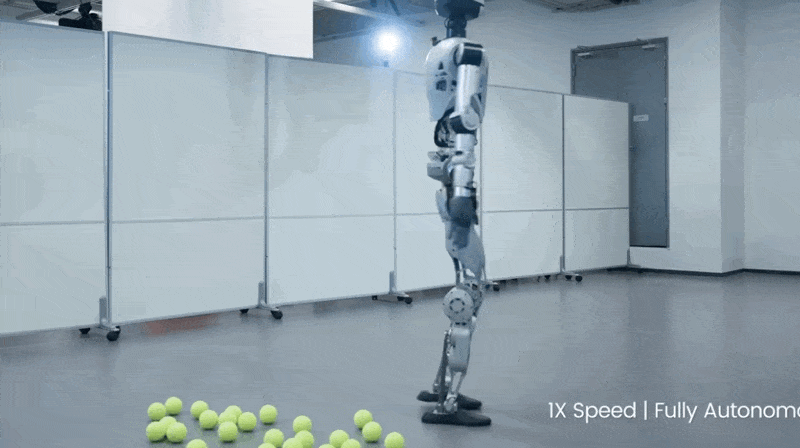
Watch this: Ball drops. Robot walks over, adjusts its stance (ADJUSTS ITS STANCE), bends down, grabs it. Walks to the basket and drops it there.
The tech making this work: 31 joints that move independently, depth cameras seeing in 3D, and algorithms processing everything simultaneously so it can walk AND grab stuff without toppling over like I do when I try to pick something up while walking.
They call it "whole-body loco-manipulation" which is fancy talk for "doing multiple hard things at once without faceplanting."
Honestly this robot has better coordination than me before my morning coffee and I'm not okay with that 😪
4. Japan Made Something Levitate with ZERO Friction (This Breaks Physics... Almost)
Okay so levitation isn't just for magic tricks anymore. Japanese scientists at OIST just made a graphite disk float and spin with basically zero friction, and I need you to understand how absolutely crazy this is.
Here's the problem they solved: when you levitate something using magnets, moving it creates these tiny circular currents called eddy currents. Think of them like invisible friction fighting against motion. They're super useful for train brakes and power tools, but for precision levitation? Total nightmare.

Previous attempts tried mixing graphite with silica powder and wax to reduce eddy currents, but that weakened the levitation force. Like solving one problem by creating another.
The breakthrough? Make it spin instead of moving up and down. A one-centimeter graphite disk spinning above rare-earth magnets stays in the same magnetic field strength the entire time. No changing magnetic flux = no eddy currents = no friction. It's all about rotational symmetry.
They proved it works through simulations, math, and actual experiments. The rotor just... spins freely without losing energy.
Practical applications? Ultra-precise gyroscopes and sensors. They already sent an earlier version to space for dark matter experiments.
Sometimes the solution is just changing the direction of movement. Who knew?
They Just Turned Plastic Bags Into Glowing Water Sensors
You know those plastic bags stuffed under your sink? The ones you keep "just in case" and now you have like 50 of them stored inside each other like some kind of recursive nightmare?
Indonesian researchers just figured out how to turn them into glowing nanoparticles that detect toxic metals in drinking water. And I'm not talking about melting them into new plastic shapes. We're talking ACTUAL NANOTECHNOLOGY made from grocery bags.
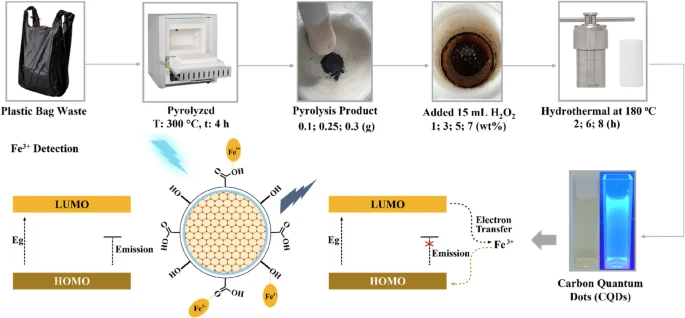
The pyrolysis-hydrothermal combo that works
The process is surprisingly elegant?
They take regular polyethylene shopping bags and hit them with pyrolysis (cooking plastic without oxygen to break down polymer chains) followed by hydrothermal treatment (high-pressure, high-temperature water environment) with less than 7% hydrogen peroxide.
Ten hours later, you get carbon quantum dots (CQDs): tiny particles between 1.5 to 4.5 nanometers. That's smaller than a virus. Under UV light, these things glow with 10% quantum yield, which is actually bright enough to function as sensors.
Traditional CQD production uses expensive or toxic materials. This uses literal garbage from your kitchen.
How the detection actually works
The CQDs have oxygen groups on their surface (carboxyl, carbonyl, hydroxyl) that selectively bind to Fe³⁺ ions (ferric iron). When Fe³⁺ attaches, it quenches the fluorescence through electron transfer.
Translation: the glow dims when there's iron in the water. Strong glow means clean water, weak glow means contamination.
They tested it down to 9.50 µM concentrations with 0.9983 correlation coefficient. That's legitimately good precision for sensors made from shopping bags. Plus they're selective: they respond to Fe³⁺ but ignore other metal ions, so no false positives.
Why this matters beyond the cool factor
Heavy metal contamination in drinking water is a massive global problem. Traditional testing needs expensive lab equipment and trained technicians. You can't test water quality in remote villages.
This approach uses waste plastic that's everywhere, requires relatively simple equipment, and creates portable sensors that work in field conditions. The CQDs stay stable under UV light, work across different salt levels, and remain functional during long-term storage.
We're turning one environmental crisis (plastic waste) into a solution for another (water safety monitoring). Bags that would sit in landfills for 500 years can instead protect public health.But I yet wonder if this has any benefits for the aquatic life (I doubt)
Your next adventure?
⦁ Boston Dynamics - Engineering Manager for Atlas Humanoid Robot program
The company building those viral dancing robots.
⦁ Axiom Space - Head of engineering at Bruz, France
Literally building commercial space stations.
⦁ SpaceX - Data Engineer in Redmond, United States
Working on the engines that'll take us to Mars.
Want to post a job to an audience of over 80k engineers? Click here to book a call with me to see how we can partner to help!