spot alzheimer before symptoms..
Current detection methods only tell you proteins are clumping somewhere, but...

Wow. A LOT of replies.
Thank you to those who attempted the game.
To continue the trend, we will have another mystery gift this week (this one’s different)!
Want to get featured in the next edition and get the mystery gift?
Let’s get into this week’s game!
Engineering Speed Round:
- I store electrical energy but I'm not a battery. I charge up instantly and release power just as fast. I'm hiding in every electronic device you own, smoothing out voltage spikes and powering camera flashes. I can kill you even when the power is off. What am I?
- I make hot things cold and cold things hot without ever mixing them together. I'm coiled up in your car's radiator, your home's AC unit, and inside power plants. I transfer heat but never the fluids themselves. What am I?
- I spin to stay perfectly still. The faster I rotate, the more I resist being pushed around. I keep ships steady in rough seas, guide rockets to space, and help your phone know which way is up. Disturb my spin and I'll fight back with surprising force. What am I?
Know the answers?
Drop them below and you might just snag this week's mystery engineering prize.
Reply here!
Want to reach an audience of over 80k engineers? Click here to book a call with me to see how we can partner to help!
What Happened This Week?
1. Your Robot Hand Just Tricked Your Brain Into Thinking It's Yours
You know that feeling when you've been typing so long your keyboard starts feeling like part of your body?
Italian researchers just proved this isn't your imagination and it works with robot hands too.
They had volunteers team up with iCub, a child-sized humanoid robot, to slice soap bars by taking turns pulling a steel wire. Sounds like the world's weirdest cooking show.
Here's what happened: your brain creates a "body schema", basically an unconscious GPS map of where your limbs are. This mental map can expand to include tools, which is why tennis rackets feel like arm extensions after a while.
The researchers used something called the Posner cueing task (flashing lights near hands to test reaction speed) to see if people's brains adopted the robot's hand as their own.
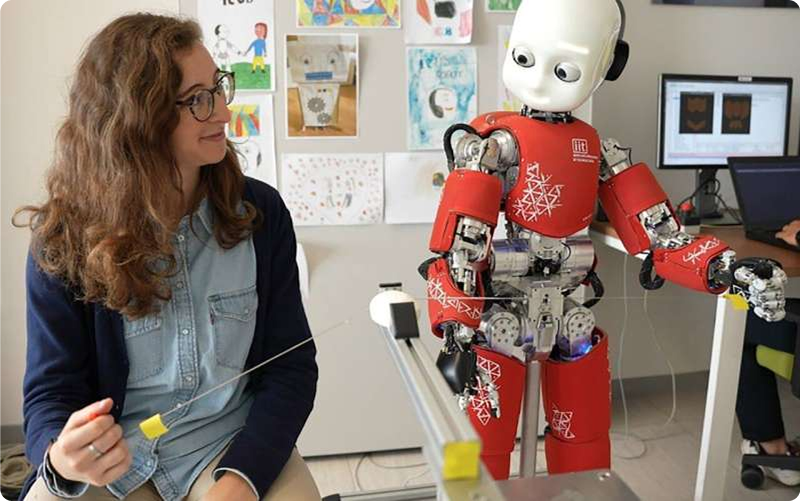
The result: your brain started treating the robot hand as part of your body, but only when iCub moved smoothly and stayed physically close.
The robot's skill level directly affected how much your brain bonded with it. Better teamwork meant stronger mental connection.
This breakthrough is huge for prosthetics design: imagine artificial limbs that feel natural instead of foreign.
Though I'm still processing the fact that my brain can be tricked by a soap-slicing robot 😢
2. Solar Glass That Fixes Itself When You Heat It to 392°F
Solar panels break.
Then you throw them away and buy new ones.
That's been the cycle for decades.
Chinese researchers just created solar glass that repairs itself.

They created this using ETP2SbCl5 phosphor (try saying that five times fast) instead of expensive nanocrystals. When the glass gets damaged, just heat it to 200°C and molecular magic happens: the material reorganizes itself and structural cracks disappear.
The glass absorbs UV light, converts it to the visible spectrum, then channels that energy to solar cells through total internal reflection.
Even after 10 heating cycles, it keeps 95% performance while staying 78% transparent.
They basically engineered glass that's too stubborn to stay broken. My phone screen is officially jealous 😅
3. Jack Ma's 243-Pound Robot Butler Cooks Shrimp Better Than Most Humans
Yup… That happened.
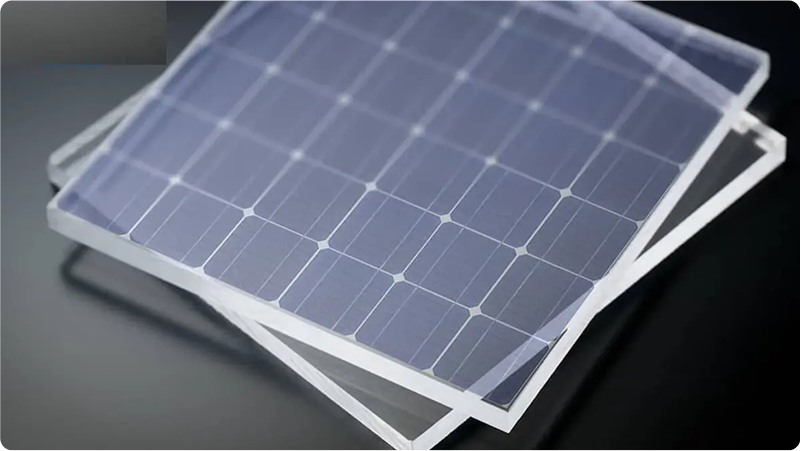
Jack Ma's Ant Group (the same guy behind Alibaba) unveiled R1, a 243-pound humanoid robot that cooked garlic shrimp at tech fairs while humans watched and questioned their life choices.
The engineering breakthrough is multi-modal sensor fusion: R1 combines force feedback, thermal monitoring, and computer vision for delicate food handling. Its algorithms coordinate 34 servo motors while Ant's AI interprets recipes and makes real-time cooking adjustments.
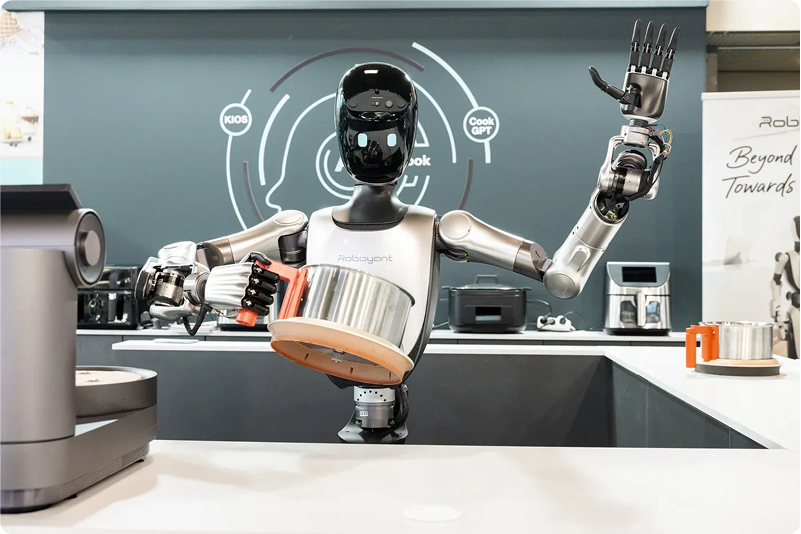

And ummm.. R1 isn't a prototype. It's mass-produced and already working at Shanghai History Museum, doing tours and basic medical consultations.
Ant Group calls themselves "robotics newcomers" but somehow shipped cooking robots before most companies delivered walking demos.
They're using their payment platform expertise (and a lot of data they have over the decades) to optimize robot-human interactions.
If robots can make restaurant-quality shrimp, I'm officially running out of useful skills.
Maybe I should learn to code... oh wait, they probably do that too 😩
Scientists Built a Molecular Magnifying Glass That Spots Alzheimer’s Before Symptoms
I’m not sure how many of you have had someone in your family with Alzheimer's, but it really pinches you on life.
One day they’re extremely sharp, another they’re struggling with your name.
Sometimes you think, man I should have spent more time.
The others you wonder how they must be struggling.
I came across this research paper from Rice University and turns out the damage was building for decades. We just couldn’t see it happening.
What if I told you that’s about to change completely?
The invisible problem killing brain cells
Inside your brain, millions of proteins are folding into perfect shapes every single second. When they fold correctly, your thoughts flow smoothly.
When they don’t, they start sticking together like wet pasta left too long in the pot.
These protein clumps eventually become the tangles and plaques that destroy brain cells in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
The issue that researchers have been trying to solve for decades is time taken to detect these clumps. As the longer we take, the more your brain has lost function.
Current detection methods only tell you proteins are clumping somewhere, but not where it starts, how it spreads, or most importantly, how to stop it early.
The breakthrough
The Rice team, led by Professor Han Xiao, engineered something that sounds like fiction: a molecular flashlight called AnapTh that changes color based on what’s happening around it.

Think of it as the world’s tiniest mood ring.
Using a technique called genetic code expansion, they can insert this probe at any specific spot in a protein without disrupting its normal function.
When proteins start acting up, the probe immediately shifts its fluorescent signature (changes color).
The shocking truth about how brain diseases actually start
Everyone assumed protein aggregation happens uniformly. We were completely wrong.
Zhang’s molecular magnifying glass revealed that problems begin at specific “hot spots” while the rest of the protein stays perfectly normal. Some regions become crowded and water-repelling, others remain unchanged.
Translation: we aren’t decaying slowly, it’s disease that spreads further and further (like a fire in a forest).
Why this could save millions of brains
This changes everything.
Instead of waiting until symptoms appear, we could potentially catch Alzheimer’s 20 years early, right when those first hot spots light up.
We’re talking about shifting from “detect and treat” to “predict and prevent.”
Imagine routine checkups that spot brain disease decades before any memory problems begin.
We just went from fighting brain disease with a blindfold on to having X-ray vision.
Your next adventure?
⦁ Electrical Engineer - Viking Masek Packaging Technologies
PLC whisperer who teaches packaging robots to wrap your snacks without having emotional breakdowns.
⦁ Civil Engineer - Chicago Transit Authority (RM Chin and Associates)
Red Line extension maestro - conducting utilities and drainage so Chicago's busiest rail keeps rolling south.
⦁ Mechanical Engineer IV - Sparton Corporation
Designing underwater spy gadgets that make submarines impossible to hide.
Want to post a job to an audience of over 80k engineers? Click here to book a call with me to see how we can partner to help!